Introduction to RF communication
This post introduces the basics of RF communication along with various band specifications used for wireless communication. It also covers comparison of different bands on basis of their data rates and other parameters.
Content
- Introduction
- Available frequency Bands
- Types of RF communication
- Different wireless protocols
Introduction
Now a days, we are surrounded by a large number of wireless devices working on different protocols, on different frequency bands thus utilizing almost whole of the "Radio-wave" frequency spectrum.
Adhering to it's high density, complete frequency spectrum can be divided into different groups and each group can be further divided into different channels.
 | |
| TI education program |
 |
| http://www.ni.com/cms/images/devzone/tut/a/706afe69127.gif |
Considering the above distribution, most of the wireless devices works in the VHF and UHF bands. Working on such high frequencies has some of it's renowned advantages like decreased antenna size, low interference from power devices, efficiency in propagation (low dispersion) etc.
Propagation at lower frequencies reduces dependencies on line-of-sight communication (As they get reflected from ionosphere). They are characterized by narrow bandwidth(usually 10%), higher bandwidths might reduce performance.
VLF and LF links usually carry low-rate digital signals or Morse code, while MF links are wide enough to carry voice signals. Above approximately 30 MHz, radio transmissions pass through the ionosphere, so higher frequency signals cannot propagate through ionospheric hops. They operate on line-of-sight or near line-of-sight propagation paths.
VHF and UHF support enough bandwidth to carry not only voice and data, but also video signals—including commercial television broadcasts.
Microwave frequencies are used to carry high information content signals in wide bandwidths. Wide band microwave point-to-point links carry large blocks of telephone signals, television signals, and wide band digital data. Communication satellite links are also at microwave.
For analysis of frequency domain, we usually prefer decibel scale since it allows a wide range of frequency components to be represented on a single scale!
Radio wave frequency band extending from 9Khz to 400Ghz can be broadly divided into three bands namely permeable, semi-permeable and LOS band.
Some of the frequency ranges from above spectrum is available for general purpose use without license. Here's the list of such unlicensed bands:
Frequency Band: 865-867 MHz
Propagation at lower frequencies reduces dependencies on line-of-sight communication (As they get reflected from ionosphere). They are characterized by narrow bandwidth(usually 10%), higher bandwidths might reduce performance.
VLF and LF links usually carry low-rate digital signals or Morse code, while MF links are wide enough to carry voice signals. Above approximately 30 MHz, radio transmissions pass through the ionosphere, so higher frequency signals cannot propagate through ionospheric hops. They operate on line-of-sight or near line-of-sight propagation paths.
VHF and UHF support enough bandwidth to carry not only voice and data, but also video signals—including commercial television broadcasts.
Microwave frequencies are used to carry high information content signals in wide bandwidths. Wide band microwave point-to-point links carry large blocks of telephone signals, television signals, and wide band digital data. Communication satellite links are also at microwave.
For analysis of frequency domain, we usually prefer decibel scale since it allows a wide range of frequency components to be represented on a single scale!
Availability of frequency bands in India
 |
| http://cdn.downtoearth.org.in/mobile-20110315.jpg |
Some of the frequency ranges from above spectrum is available for general purpose use without license. Here's the list of such unlicensed bands:
Frequency Band: 865-867 MHz
Low power RFID equipments or any other low power wireless devices or equipments
Power: Maximum transmitter output power of 1 Watt ( 4 Watts Effective Radiated Power)Carrier Bandwidth: 200 KHz
Reference: GSR 564 ( E) dated 30 July 2008
Frequency Band: 2.4-2.4835 GHzPower: Maximum transmitter output power of 1 Watt ( 4 Watts Effective Radiated Power)Carrier Bandwidth: 200 KHz
Reference: GSR 564 ( E) dated 30 July 2008
Use : Low power equipments
Power: Maximum transmitter output power of 1 Watt ( 4 Watts Effective Radiated Power)
Carrier Bandwidth: spectrum spread of 10 MHz or higher
Reference: GSR 45E dated 28.1.2005
Frequency Band: 5.150-5.350 GHz, 5.725 - 5875
Use : Low power equipments for Cellular telecom systems including Radio Local Area Networks, Indoor applications
Power: maximum mean Effective Isotropic Radiated Power of 200mW, maximum mean Effective Isotropic Radiated Power density of 10mW/MHz in any 1 MHz bandwidth,
Carrier Bandwidth: 1MHz
Reference: GSR No 46E dated 28.1.2005
Frequency Band: 5.825 to 5.875 GHz
Use : Low power equipments
Power: maximum transmitter output power of 1 Watt ( 4 Watts Effective Radiated Power)Carrier Bandwidth: spectrum spread of 10 MHz or higher
Reference: GSR no 38E dated 19.1.2007
Frequency Band: 26.957-27.283 MHz
Use : Wireless equipments intended to be used while in motion or during halts
Power: maximum Effective Radiated Power ( ERP) of 5 Watts
Reference: GSR no 35 E dated 10.01.2007
Frequency Band: 335.7125, 335.7375,335.7625, 335.7875, 335.8125 and 335.8375MHz
Use : Low power equipments for the remote control of cranes
Power: maximum transmit power of 1mW
Carrier Bandwidth: 10 KHz
Reference: GSR 34( E) dated 10.1.2007 and GSR 532 ( E) dated 12.8.2005
Power: Maximum transmitter output power of 1 Watt ( 4 Watts Effective Radiated Power)
Carrier Bandwidth: spectrum spread of 10 MHz or higher
Reference: GSR 45E dated 28.1.2005
Frequency Band: 5.150-5.350 GHz, 5.725 - 5875
Use : Low power equipments for Cellular telecom systems including Radio Local Area Networks, Indoor applications
Power: maximum mean Effective Isotropic Radiated Power of 200mW, maximum mean Effective Isotropic Radiated Power density of 10mW/MHz in any 1 MHz bandwidth,
Carrier Bandwidth: 1MHz
Reference: GSR No 46E dated 28.1.2005
Frequency Band: 5.825 to 5.875 GHz
Use : Low power equipments
Power: maximum transmitter output power of 1 Watt ( 4 Watts Effective Radiated Power)Carrier Bandwidth: spectrum spread of 10 MHz or higher
Reference: GSR no 38E dated 19.1.2007
Frequency Band: 26.957-27.283 MHz
Use : Wireless equipments intended to be used while in motion or during halts
Power: maximum Effective Radiated Power ( ERP) of 5 Watts
Reference: GSR no 35 E dated 10.01.2007
Frequency Band: 335.7125, 335.7375,335.7625, 335.7875, 335.8125 and 335.8375MHz
Use : Low power equipments for the remote control of cranes
Power: maximum transmit power of 1mW
Carrier Bandwidth: 10 KHz
Reference: GSR 34( E) dated 10.1.2007 and GSR 532 ( E) dated 12.8.2005
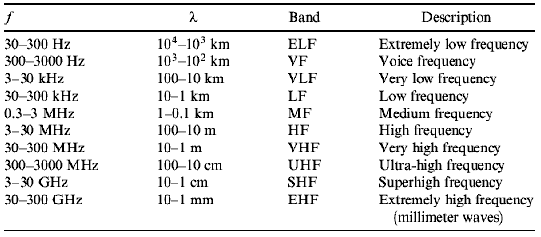
IEEE further divided RF bands as per their standard.
 | |
| wikipedia |
Types of RF communication
There are broadly two types of RF communications: Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex mode.
Half-Duplex Mode
In this mode of transmission, device cannot transmit and recieve data simultaneously. For example: walkie-Talkie.
Full-Duplex Mode
In this mode of transmission, device can simultaneously transmit and receive data. It's usually done via reserving two frequency channels one for transmitting and other for receiving. For example: Mobile phones
Different Wireless protocols
Various protocols like 802.11(WiFi), bluetooth, nfc, Wimax,GSM/EDGE,CDMA,TDMA,AM, FM, RDS, XM, Sirius,tire pressure monitoring (TMPS),zigbee, BLE are used for communication over radio frequencies. They vary in their efficiency, data rate, bandwidth, range, error correction-detection algo. etc.
802.11 a/b/g/n/ac:
802.11 was initially developed in 1997, but due to it's very low bandwidth(~2Mbps) it was initially rejected. After few years, with some improvement in bandwidth(upto 11 Mbps) 802.11b was launched, but since it was working on 2.4Ghz, it suffered interference from regular home appliances like Microwave oven. In same year 802.11a was launched which worked on 5Ghz, with improved speed it's incompatible with 802.11b , short-ranged and costly.
With some several changes in packet exchanging algorithm, 802.11 g was developed with maximum speed of 54Mbps.
MIMO(Multiple input Multiple output) technology implemented along 802.11g gives 802.11 n with very high bandwidth and speed. Latest version 802.11 ac supports both 2.4 and 5 Ghz and is thus backward compatible with both 802.11b/g and 802.11a.
http://www.techrepublic.com/article/solutionbase-80211g-vs-80211b/
LINK:http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/802/11/Reports/802.11_Timelines.htmBluetooth,BLE(Bluetooth 4.0):
Bluetooth supports a very short range (approximately 10 meters) and relatively low bandwidth (1-3 Mbps in practice) designed for low-power and cheap network devices like handhelds and wearable devices.NFC(Near field communication) :
Evolved from RFID, NFC uses very low power chips that can transfer data at a very high speed when held at a close proximity(4 cm).
NFC device is also used in contact less payments.NFC employs electromagnetic induction between two loop antennas when NFC-enabled devices—for example a smart phone and a printer—exchange information, operating within the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band of 13.56 MHz on ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface at rates ranging from 106 to 424 kbit/s.
WiMAX(Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access):
WiMAX( IEEE 802.16) is much more then just implementation of WiFi on a larger scale, for wireless Metropolitan Area Network(MAN). It aims at interoperability of different standards and providing an alternative to DSL and cable.It was once a competitor for 4G. Latest version provides an increased bandwidth of ~1Gbps.
Mobile WiMAX was a replacement candidate for cellular phone technologies such as GSM and CDMA, or can be used as an overlay to increase capacity. Fixed WiMAX is also considered as a wireless backhaul technology for 2G, 3G, and 4G networks in both developed and developing nations.GSM,EDGE,CDMA,TDMA:
GSM(Global system for mobile) is the most popular and widely used cellular standard after CDMA. It offers wider international roaming, data usage along with calling capability and advantage of easily swapable SIM card.
In India, GSM telephony works on two different frequency bands GSM900 and GSM1800 in MHz(mega hertz). Lower frequency network bands offers higher coverage while higher frequency network bands offers higher data speeds.
EDGE(Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) is an improvement over GSM providing speed upto 384 Kbps. Latest version of EDGE is twice faster. It's builds upon enhancements provided by general packet radio service (GPRS) and high-speed circuit switched data (HSCSD).
CDMA(Code Division Multiple Access) is a technology competing with GSM and is now incorporated in UMTS(Universal Mobile Telecommunication system)(3G). It uses codec to multiplex calls over same frequency bands.
TDMA(Time Division Multiple Access) multiplex data in time domain and is incorporated in GSM(2G).ZIGBEE(IEEE 802.15.4):
Developed as an open global standard for low cost,low power M2M communication between MCU's in harsh environment, ZigBee operates on IEEE 802.15.4 supporting almost all unlicensed frequencies 868Mhz,900Mhz and 2.4 Ghz.
Zigbee protocol features include:
- Support for multiple network topologies such as point-to-point,
point-to-multipoint and mesh networks - Low duty cycle – provides long battery life
- Low latency
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
- Up to 65,000 nodes per network
- 128-bit AES encryption for secure data connections
- Collision avoidance, retries and acknowledgements
REFERENCES:
- http://www.ni.com/tutorial/3541/en/
- http://www.ti.com/lit/ml/slap127/slap127.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radio_spectrum#IEEE
- http://cdn.downtoearth.org.in/mobile-20110315.jpg
- http://www.indiasemiconductorforum.com/wirelesss/321-list-licence-free-frequencies-india-wireless-usage.html
- https://www.iotforall.com/ieee-protocols-zigbee-wifi-bluetooth-ble-wimax/




Comments
Post a Comment